Shared Hosting vs. VPS vs. Cloud Hosting: Which One is Right for You?
Choosing the right web hosting is one of the most critical decisions you'll make when starting a new website. The type of hosting you select impacts your site's performance, security, scalability, and cost. However, with terms like Shared, VPS, and Cloud, the options can be overwhelming for beginners.
This guide will break down the three most popular types of web hosting in simple terms, using easy-to-understand analogies, so you can confidently choose the perfect plan for your project's needs.
1. Shared Hosting: The Apartment Building
The Analogy: Think of Shared Hosting as living in an apartment building. You have your own apartment (your website), but you share the building's main resources—like the water supply, electricity, and elevator (the server's CPU, RAM, and disk space)—with all the other tenants. It's the most affordable and common entry point.
What It Is
Shared Hosting is where multiple websites reside on a single physical server. All these websites share the same server resources. It's an economical solution because the cost of the server is split among all the users.
Pros:
- Most Affordable: The cheapest hosting option available.
- Beginner-Friendly: Typically comes with a control panel (like cPanel) that makes managing your website easy, even without technical skills.
- Maintenance-Free: The hosting provider handles all server maintenance, security updates, and administration.
Cons:
- Limited Resources: A sudden traffic spike on another website on your server (a "noisy neighbor") can slow your website down.
- Less Secure: While providers have security measures, a security breach on one site could potentially affect others on the same server.
- Poor Scalability: Not suitable for websites with high or rapidly growing traffic.
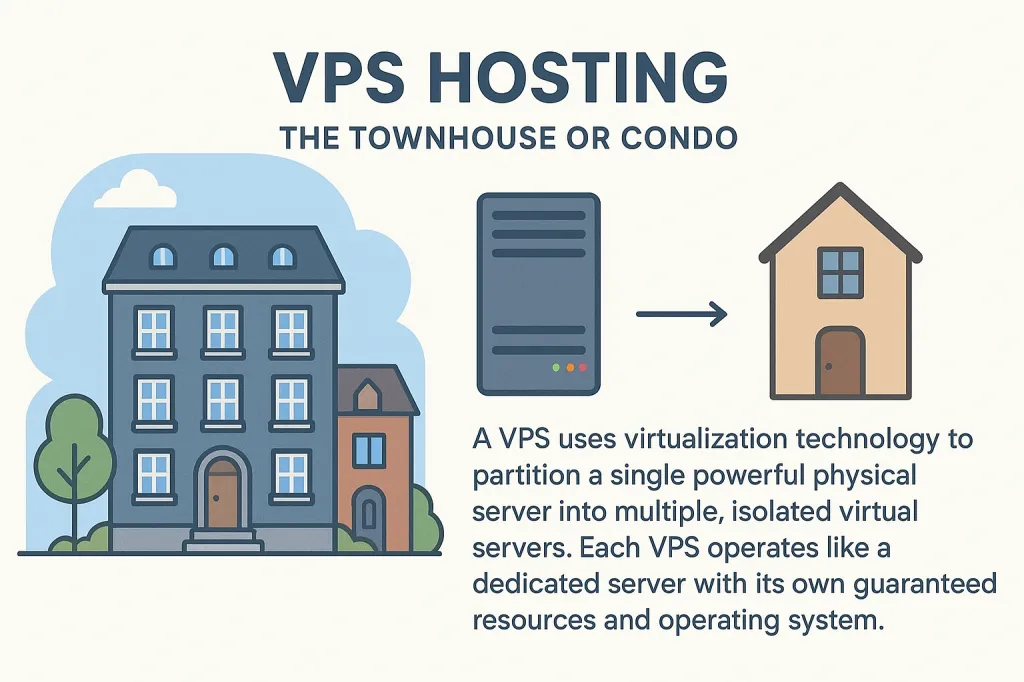
2. VPS Hosting: The Townhouse or Condo
The Analogy: A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is like owning a townhouse or a condo. You're still part of a larger building (the physical server), but your unit is completely private. You have your own guaranteed utilities and space (dedicated RAM and CPU), and your neighbors' activities don't directly affect you. You have more control but also more responsibility.
What It Is
A VPS uses virtualization technology to partition a single powerful physical server into multiple, isolated virtual servers. Each VPS operates like a dedicated server with its own guaranteed resources and operating system.
Pros:
- Guaranteed Resources: Your site's performance is not affected by other users.
- Greater Control & Flexibility: You typically get root access, allowing you to install custom software and configure the server environment to your exact needs.
- Improved Security: The isolated nature of a VPS makes it more secure than shared hosting.
- Scalable: You can easily upgrade your resources (RAM, CPU) as your website grows.
Cons:
- More Expensive: Costs significantly more than shared hosting.
- Requires Technical Knowledge: You are responsible for managing and securing your virtual server, which requires technical expertise. (Note: "Managed VPS" plans exist where the provider handles this for you at a higher cost.)
3. Cloud Hosting: The Modern Utility Grid
The Analogy: Cloud Hosting is like a futuristic power grid. Instead of relying on a single power plant, your electricity is drawn from a vast, interconnected network of plants. If one plant goes down, the grid automatically reroutes power from others, ensuring you're never without electricity. You get ultimate reliability and often pay only for what you use.
What It Is
Cloud Hosting uses a cluster of connected servers (the "cloud") that work together to host a group of websites. Your site's data and resources are spread across multiple servers, providing excellent reliability and scalability.
Pros:
- Superior Uptime & Reliability: If one server fails, your site is automatically moved to another server in the cluster with no downtime.
- *
Ultimate Scalability:
- You can scale your resources up or down almost instantly to handle massive traffic spikes. *
Flexible Pricing:
- Often uses a "pay-for-what-you-use" model, which can be cost-effective for some.
Cons:
- Can Be Expensive: The costs can be higher and less predictable than fixed-price plans.
- Complex to Manage: Often requires a high level of technical expertise to configure and manage effectively.
At a Glance: Comparison Table
| Feature | Shared Hosting | VPS Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analogy | Apartment | Townhouse / Condo | Utility Grid |
| Cost | $ (Lowest) | $$ (Medium) | $$$ (Variable/High) |
| Performance | Basic | Good / Guaranteed | Excellent / High-Traffic |
| Ease of Use | Very Easy | Medium / Technical | Difficult / Technical |
| Scalability | Low | Good | Excellent |
| Best For | Beginners, Blogs | Growing Businesses | Mission-Critical Apps |
There is no single "best" hosting type—only the best one for you. The right choice depends entirely on your project's needs, your budget, and your technical comfort level. A great strategy for many is to start with a quality Shared Hosting plan and upgrade to a VPS as your website traffic and needs grow.